What Are The Phase Changes Of Matter When You Increase Energy
Phases of Thing – Gas, Liquids, Solids
To view these resources with no ads, please Login or Subscribe (and help support our site).
Focus Questions and Goals
one) What is matter?
two) Name the three phases (states) of matter?
3) Place and describe the particle in each phase of affair and how they are different in each phase of matter.
About Matter
Matter is something that has mass and book (takes upwards space). Affair can be institute in several phases or states. The iii well-nigh mutual phases of matter on Earth are solids, liquids and gases. Less commonly, we can also observe thing as plasma or Bose-Einstein (Exist) condensate.
Solids have a stock-still shape and volume. A solid'due south particles are packed closely together. There is not much space betwixt the particles and there is petty particle move. A solid is not easily compressed.
Liquids have a fixed volume, only accept the shape of the container in which they sit. In that location is non much space between the particles, but they tin slide past each other and flow easily. A liquid is non hands compressed.
Gas fills the shape and book of the container in which it sits. At that place is a lot of free space between its particles and they flow easily past each other. Gas tin exist compressed.
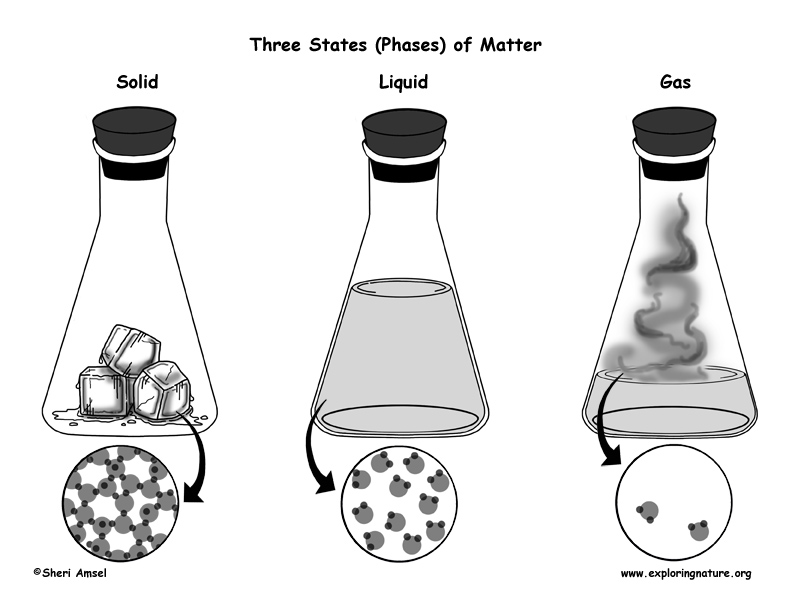
These are physical states of the molecules of thing. Molecules can shift from one concrete state to another without changing their molecular construction (or chemical state). Water is still Hii0 when it is water ice, steam or a liquid – even though its physical country has changed.
Physical states can be inverse by adding energy (i.e. increasing temperature or pressure) or releasing energy (i.e. cooling or lowering force per unit area). This does non change the matter'southward molecular structure. It is even so the aforementioned affair or substance. When you lot heat a substance, yous are adding free energy to it. The movement of its molecules will increment until its concrete state changes.
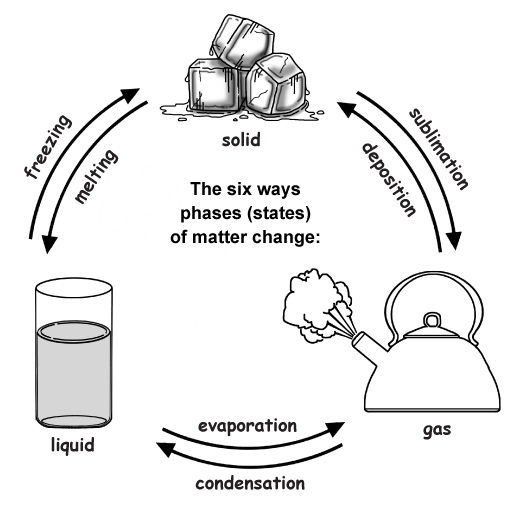
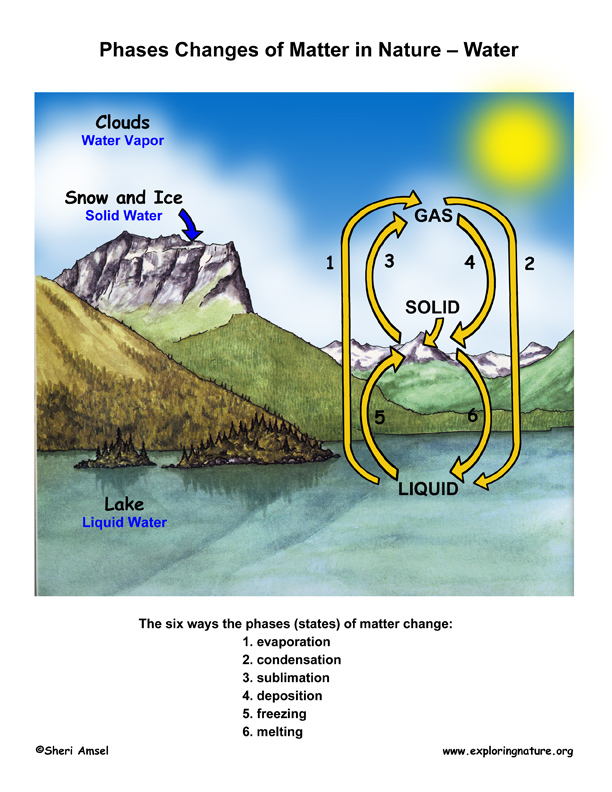
The half dozen means to modify the stage (state) of thing:
i) Melting changes a solid to a liquid. (i.e. dripping icicles)
2) Freezing changes a liquid to a solid. (i.east. lake freezing over)
3) Evaporation changes a liquid to a gas. (i.east. apparel drying on a clothesline)
4) Condensation changes a gas to liquid. (i.e. water forming on the outside of a cold drinking glass)
v) Sublimation changes a solid to a gas. (i.eastward. water ice cubes shrinking in the freezer)
6) Degradation changes a gas to a solid. (i.eastward. frost forming on the windows)
These changes happen at precise temperatures for dissimilar substances. Scientists refer to these as melting point, freezing betoken, condensing point and humid point. H2o'southward melting point is 0°C, while its boiling signal is 100°C.
Water's Unique Quality
Usually solids are more than dense than liquids because their molecules are closer. Water is an important exception to this rule. When water freezes, it forms a bonded arrangement of molecules that is actually less dumbo than liquid water, yet takes up more space. This is an important feature of water in that when water ice forms on a lake or other waterway, it is less dumbo than the liquid water – so forms on top of the liquid water. This allows h2o animals to stay alive all wintertime under the ice. Without this trait, many of the living things on Globe would not have survived and evolved to what we have today.
It is as well important to note (and helpful to us) that other substances take much higher melting temperature than h2o. Imagine if common salt or saccharide melted at room temperature the way water does.


To view these resources with no ads, please Login or Subscribe (and help back up our site).
Please Login or Subscribe to access downloadable content.
Please Login or Subscribe to access downloadable content.
Citing Research References
When you enquiry information yous must cite the reference. Citing for websites is unlike from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Fashion Citations (Mod Linguistic communication Clan).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Proper name, Offset Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if advisable." Championship: Subtitle: Section of Folio if advisable. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Terminal Updated. Day Calendar month Twelvemonth of admission < URL >.
Here is an example of citing this page:
Amsel, Sheri. "Phases of Matter – Gas, Liquids, Solids" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2022. April 17, 2022
< http://world wide web.exploringnature.org/db/view/Phases-of-Matter-ndash-Gas-Liquids-Solids >
What Are The Phase Changes Of Matter When You Increase Energy,
Source: https://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Phases-of-Matter-ndash-Gas-Liquids-Solids
Posted by: combsobjer1979.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Are The Phase Changes Of Matter When You Increase Energy"
Post a Comment